Problems with
Semaphores
·
Correct
use of semaphore operations:
o
signal
(mutex) …. wait (mutex)
o
wait
(mutex) … wait (mutex)
o
Omitting of wait (mutex) or signal (mutex) (or both)
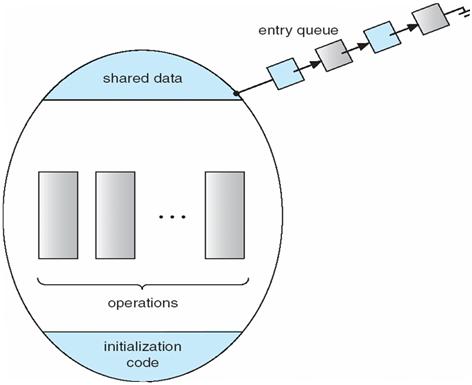
Monitors
·
A
high-level abstraction that provides a convenient and effective mechanism for
process synchronization
·
Only
one process may be active within the monitor at a time
monitor monitor-name
{
//
shared variable declarations
procedure P1 (…) { …. }
…
procedure Pn (…) {……}
Initialization code ( ….) { … }
…
}
Schematic view of a
Monitor
Condition Variables
·
condition
x, y;
·
Two
operations on a condition variable:
o
x.wait
() – a process that invokes the
operation is suspended.
o
x.signal
() – resumes one of processes (if any) that invoked x.wait ()
Monitor with Condition
Variables
Solution to Dining
Philosophers
monitor
DP
{
enum { THINKING; HUNGRY, EATING)
state [5] ;
condition self [5];
void pickup (int i) {
state[i] = HUNGRY;
test(i);
if (state[i] != EATING) self [i].wait;
}
void putdown (int i) {
state[i] = THINKING;
// test left and right
neighbors
test((i + 4) % 5);
test((i + 1) % 5);
}
void test (int i) {
if ( (state[(i + 4) % 5] != EATING)
&&
(state[i] == HUNGRY) &&
(state[(i + 1) % 5] != EATING) ) {
state[i] = EATING ;
self[i].signal () ;
}
}
initialization_code() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
state[i] = THINKING;
}
}
·
Each
philosopher I invokes the operations pickup() and putdown() in the following sequence:
DiningPhilosophters.pickup (i);
EAT
DiningPhilosophers.putdown (i);
Monitor Implementation
Using Semaphores
·
Variables
semaphore
mutex; // (initially = 1)
semaphore
next; // (initially = 0)
int
next-count = 0;
·
Each
procedure F will be
replaced by
wait(mutex);
…
body of F;
…
if
(next_count > 0)
signal(next)
else
signal(mutex);
·
Mutual
exclusion within a monitor is ensured.
Monitor Implementation
·
For
each condition variable x, we
have:
semaphore
x_sem; // (initially = 0)
int
x-count = 0;
·
The
operation x.wait can be implemented as:
x-count++;
if
(next_count > 0)
signal(next);
else
signal(mutex);
wait(x_sem);
x-count--;
·
The
operation x.signal can be implemented as:
if (x-count > 0) {
next_count++;
signal(x_sem);
wait(next);
next_count--;
}
A Monitor to Allocate
Single Resource
monitor
ResourceAllocator
{
boolean busy;
condition x;
void acquire(int time) {
if (busy)
x.wait(time);
busy = TRUE;
}
void release() {
busy = FALSE;
x.signal();
}
initialization
code() {
busy = FALSE;
}
}